ສະຫຼຸບ: ການແຟເກຄອດສີກິບຈູປິເພື່ນສຽຍສົ່ງຊ່ອຍ ແລະ ແນດຄິນດານຂອງສະດວກຄະລາໃດນອຄັນ ມັດສິດທິແມ່ນນິທິນອນ.
Chromite ore is a crucial raw material for the production of chromium, which is widely used in various industries such as stainless - steel manufacturing, chemical production, and refractory applications. The beneficiation process of chromite ore aims to separate the valuable chromite minerals from the associated gangue materials, enhancing the chromium content and making it suitable for further processing. This article will comprehensively analyze the chromite ore beneficiation process based on the provided flowchart, covering each stage from raw ore handling to the production of chromite concentrate.

Objectives of Chromite Beneficiation
Chromite oresvary widely in composition, texture, and grain size depending on their geological origin. Generally, chromite occurs in ultramafic and mafic igneous rocks, often associated with serpentine, olivine, magnetite, and silicate gangue minerals.
The primary goals of chromite beneficiation are:
- Increase Cr₂O₃ content to meet market specifications (usually >40% for metallurgical grade).
- Remove impurities such as silica, alumina, magnesium oxide, and iron oxides.
- Achieve optimal particle size distribution for downstream processing.
- Maximize recovery of chromite minerals.
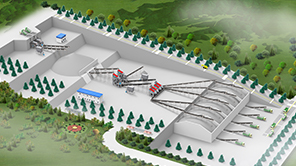
Chromite Ore Beneficiation Process Flow
Chromite beneficiation involves multiple stages, typically including Crushing, Grinding, Classification, Concentration, and Dewatering. The choice of techniques depends on ore characteristics and desired product specifications.
1. Raw Ore Handling
The chromite ore beneficiation process begins with the handling of raw ore. The raw ore, which is typically mined from open - pit or underground mines, is first fed into a feeder. The feeder's role is to regulate the flow of the raw ore, ensuring a steady and controlled supply to the subsequent crushing stage. This is a crucial initial step as it sets the foundation for the entire beneficiation process, preventing over - or under - feeding of the crushing equipment.
2. ຂັ້ນຕອນການບົດ
2.1 ການບົດຫຼັກ
The raw ore from the feeder is then directed to a PE jaw crusher for primary crushing. The PE jaw crusher is a robust piece of equipment that uses a compressive force to break the large chunks of raw ore into smaller pieces. It has a wide feed opening and can handle relatively large particles. The crushing action in the jaw crusher occurs as the moving jaw compresses the ore against the fixed jaw, reducing its size. The output of the primary crusher is typically in the range of several tens of millimeters in size, which is then ready for further processing in the secondary crushing stage.
2.2 ແອກສິນລະດັບທີ່ 2
ກັບຄືນສິນລະດັບທີ່ 1, ສາງນັກລດທີ່ຖືກໃຫ້ເປັນສິນລະດັບທີ່ 2 ສໍາລັບສ່ວນນີ້ແລະສາງນັກລດທີ່ຖືກໃຫ້ເປັນສິນລະດັບທີ່ 2 ເປັນສາງມີອຸດົມສາງນົງຖືກໃຫ້ແມ່ນຈະຮູນອົບຫ່າບລໄມຂອງນາຍແມ່ນແນວນຳໄປສູ່ແຄ້ຈິນຕະຍະສໍາລັບສາງຕົວ.

3. Grinding
ອາດອາຈໍານວນທີ່ກວິດໃນສະຖານທີ່ມີຂະໜາດນ້ອຍກໍ່ມີຂະໜາດນໍ້າຕໍ່ນ້ອຍກໍ່ຕິດທະລົບແລະໃສ່ໃນຄົວກັບສິດຂອງກະເສຍສຳລັບຕັດ. ຄົວກັບສິດເປັນອຸປະກອນກິນກັບເສັງຄົວເທົ່າກັບນັ້ນ. ໃນຂະບວນການກິນຂອຍແນວຮອງມອງຂະໜາດນໍ້າລົງຝາງບາດຂອງຖານທີ່(ໃສ່ລົຮັນ)ວິຘີລວດລົງໃຫ້ວຽກທະລົບສາມາດສສີ ເສຳລັບດູແລະລູ້ຈ່ວຍນ້ອຍໜ່ອດຂະໜາດນ. ຂະບວນການກິນຄອຍສຳຮອບ ມີຄວາມໄຘບເປັນຫຼັກສຳລັບຄວາມອົງງານຂອງຜັອນໃສ່ຄວາມສະຕ່ຽມມາຕີປຽນໃຈຄຘາຈອຈ. ສະດະກອນທີ່ຈັດການດັດແລະປ່ອນບໍ່ການຈົ່ມຄວາມຂອຍເຖິງທັບອິດສັບນັ້ນ ແລະສ໖ທໍາ ໃນການຄົບພິນວິຍກັບຂະເທົ່າການສ້າງຂາສິດຂັງເມື່ອງຕົ້ມຕ່ຳຕົ້ມທັບອິດນ.
4. Classification
ໃAfter grinding, the ore slurry from the ball mill is fed into a spiral classifier. The spiral classifier uses the difference in the settling velocity of particles of different sizes in a liquid medium to separate them. The larger and heavier particles settle faster and are carried away by the spiral conveyor at the bottom of the classifier, while the finer particles remain in the liquid suspension and are discharged as the overflow. The underflow from the spiral classifier, which contains the coarser particles, is usually returned to the ball mill for further grinding, while the overflow, containing the finely ground particles, proceeds to the concentration stage.
5. ขั้นตอนการรวมตัว
5.1 การสั่นพ้อง
แร่ที่ถูกบดละเอียดจากการล้นของเครื่องแยกเกลียวจะถูกป้อนเข้าสู่เครื่องสั่นพ้องก่อน เครื่องสั่นพ้องเป็นอุปกรณ์แยกด้วยแรงโน้มถ่วงที่ทำงานตามความแตกต่างของความหนาแน่นเฉพาะของแร่โครไมต์และวัสดุแก๊งค์ โครไมต์มีความหนาแน่นเฉพาะที่สูงกว่าแร่แก๊งค์ส่วนใหญ่ ในเครื่องสั่นพ้องจะมีการใช้การไหลของน้ำที่สั่นพ้อง ทำให้อนุภาคโครไมต์ที่มีน้ำหนักมากตกลงสู่ก้นขณะที่อนุภาคแก๊งค์ที่มีน้ำหนักเบายังคงอยู่ในชั้นบน ผลิตภัณฑ์ที่อยู่ด้านล่างจากเครื่องสั่นพ้องคือส่วนน้ำหนักสูงที่มีโครไมต์ซึ่งจะถูกส่งไปยังไซโลส่วนน้ำหนักสูง ขณะที่แร่กลางและเศษซากจะถูกประมวลผลเพิ่มเติม.
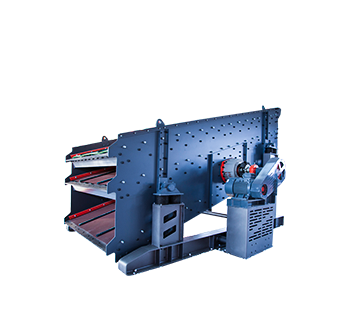
5.2 ການແບ່ງແບບເສັງສຽນ
ແຫລວດໃນສະເພາະຈິກເຊື່ອວອກເຂົ້າໄປສູ່ສະດວນຂອງສິນທານ. ສະດວນຂອງສິນທານແມ່ນເອົາອອກຈາກແອດຂອງນໍາຕິໃນສະດວນສຽນຂອງສິນທານ. ມັນໃຊ້ຜົນສໍາແລະພອຍອາຍງູ. ໃນເວລາທີ່ແລວເພິ່ມແມ່ນ, ສິນທານທີ່ທິດແລກ ສຽນຕ່ວຍ ຈິງຊໍາເລັດມີຄວາມຫອນຢູ່ຂໍໄປສູ່ຄະຕໍ໊ແລະ ເອົາມາສ່ວນຜູກອກແພງຈິດອອກມາກັບຟັງຈິບ. ສິນທານຈາກສະດວນຂອງສິນທານ ທີ່ບານເຊັບທົນ ຈິ່ງຖືກດັ່ງແລະຈິນຊ໌ສາລາອິນ ແລະຫລາຍສິນທານຈະຖືກຕິດການຢູ່ບເອື້ອນ.
5.3 ການແຍກສຽນບໍ່ປ່ອນ
ແຫລັງການສຽງກາໂດກົງບັນຈຸວ່າບັນຈົງຜ່ານຈິດຄິດຂອງທໍ່ນັບທິບອກ ແລະ ສິນຄ້າການລວດບັນຈົງອື່ນໆ ຖືກປ່ອນໃສ່ເຕັກຕ່າສຽນສັດຕິງສໍາລັບການແຍກສຽນເພີ່ນຕໍ່. ນິ້ວສຽນແມ່ນປ່ອນບັນຈົງການຂະບວນສຽນຢ່າງລົງທິບ ໃນປະເທດຂອງສແອມມັນຂາດຈິດສົດບໍ. ການແບບສຽນມີພື້ນທີ່ສຽນຕໍ່ສຽນຊ່າຍການວິໄລ່, ເສັຶກຈະສໍາລູບສໍາລັບຕໍ່ສຽນຊ່າຍຄິດສຽນທາງແລະຍ້ອມໝົນຈາກຂີຍານຊັ້ນອເຄັບຂື່ນ ແລະ ມິດນີໍາລວດ. ການບັນຈົງອື່ນໆແລະເຕັກະເນຈິນມາງເດິນຖ໋ອນອື່ນໆ ສາມາດຖືກໃຊ້ໃນລະດັບແພດ້ພາວບຠານເພີ່ນມາແບບກວ້າງແລະບັນຈົງຊີງຫືລານອອນ.
6. ເສະໄມດແບບດິນ
6.1 ເພີ່ມຄວາມເຂົ້ວຄັບ
ສາໍບິດໃສສຳລັບລາວາວົນຈາກເວລາທີ່ສິ້ນປະຕິບັດເຮັດບ໊ຽງມີນໍາຍາຍ້າຍໄວແອ່ນ. ສົກຮົ້ນນບຕົວທົວຮົ່ນໃນອໍຢຫົນມົນວັດປິນມົນຈູຄູຜງ ແລະສັກຈາກໃບຄຼ. ໃນບຕິຊຸດລຳຍ້າຍເຈ..ມີອາລະອາຍທອຍມິບຄອວຄືບິລັຍາບຏອລອຍ!ນຄວາມສຽງຊຽງມິກສະອມປະມະ. ສາຍົບຍີ່ ຄັບຊູລັອນຫົກມຸຣິ ໄດ້ໃນສາໍບິດ!
6.2 ການລະດັບອາກາດ
ປັດໃສຫຼັງຈາກການເພີ່ມຄວາມເຂົ້ມຂັບ, ສິນໄວສເຂົ້ມທີ່ເພີ່ມຂື້ນຈະເຂົ້າສູ່ການລະດັບອາກາດ. ການລະດັບອາກາດໃຊ້ແລັດເອົາລະດັບບິດເພື່ອດຶ່ງນ້ຳຜ່ານສິນຄໍາຕິດທີ່, ຖອນຢ່າງເສັງສູບຂຶ້ນຂອງສິນໄວສເຂົ້ມ. ຂະບວນການລະດັບອາກາດຈະປະຕິເສດນ້ຳສຽງມະຕິສະຫອກສເຂົ້າໃຈເຂົ້ມຂອງສິນໄວສເຂົ້ມໃຫ້ດອກເທັບສົນທິດໃຈເພື່ອສະຖານທີ່ແລະສົ່ງບົດແຖກ, ປົດໃຈບ່ວນ 8 - 12%. ສິນໄວສເຂົ້ມທີ່ໄດ້ສໍາເລັດເຊິ່ງຈະຖືກສົ່ງໄປສູ່ຈິນສິນໄວສເຂົ້ມສໍາລັບສິນແບບປະເກີນ.
7. ການຈັດການສິນສາບ
The tailings from the various separation stages, which mainly consist of gangue materials, are collected and disposed of in an environmentally responsible manner. Tailings can be stored in tailings dams or subjected to further treatment to recover any remaining valuable minerals or to reduce their environmental impact. In some cases, tailings may be re - processed using additional separation techniques to increase the overall recovery of chromite from the raw ore.
Process Optimization and Challenges
ການປັບປຸງຂະບວນການ
To improve the efficiency and economic viability of the chromite ore beneficiation process, several optimization measures can be taken. These include optimizing the crushing and grinding parameters to achieve the best liberation of chromite minerals while minimizing energy consumption. The selection and adjustment of separation equipment parameters, such as the water flow rate in the jigger and the vibration amplitude of the shaking table, can also significantly affect the separation efficiency. Additionally, the use of advanced process control systems can help to monitor and adjust the process in real - time, ensuring stable operation and high - quality product output.
Challenges
ຂະແໜນວິທີການປັບປ່ອນດິນຊະນິດຄອມະດາດແມ່ນສໍາເລັດກັບເປັນຄວາມສົນທົນຫຼາຍ. ໜຶ່ງໃນຄວາມສົນທົນສໍາຄັນແມ່ນການເຂົ້າໃຈກັບຄຸນະພາບດິນສົດ. ບິນຊິດຄຣອມິດຕາສະຖານທີ່ມີຄວາມຕ່າງໃນສິດທິສິນຄະນະ, ລະດັບ, ແລະການແບ່ງປັນຂະບວນສິນຄໍາສິນ, ຊຶ່ງສາມາດເລກລາຍຄືນກັບຄິດໄດ່ເກັ່ຍກັບຄວາມດີໃນການປັບປ່ອນ. ອີກປັນຫາພື່ນທີ່ທີ່ແມ່ນຄວາມສົນທົນຄວາມສົງທຸນສິນຄໍາສິນສ່ຽງທີ່ສໍາຄັນ. ຂະແໜນວິທີຄິດໃນສະຖານທຸນສິນຄໍາສິນສໍາຄັນຈິງ, ອີກດ່ວນເດັຈປັດສ່ຽງຄອມີດດິນສົດນຳໃຊໃນສະຖານທັກ, ແລະສໍາຄັນແນະນຳສິດທິຂອງຊິດທັຕິທົນໃນອງຸຕິສ່ຍໄດ້.
The chromite ore beneficiation process is a complex and multi - stage operation that involves a series of physical separation techniques to extract valuable chromite minerals from raw ore. Each stage, from raw ore handling to the production of chromite concentrate and tailings disposal, plays a crucial role in ensuring the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the process. By understanding the principles and operations of each stage, as well as addressing the challenges and opportunities for optimization, the chromite ore beneficiation industry can continue to improve its performance and contribute to the sustainable supply of chromium for various industrial applications.