To develop new type energy-saving, land-saving and recyclable building material to replace the traditional solid clay bricks which have been widely used, there is a series of new policies has been launched by country. The direct-controlled municipality and large and medium-sized coastal cities will forbid using the solid clay bricks to promote the modernization of housing industry and improve the residential quality.
-
Aerated concrete has been popular in market due to its unique features of land protecting, environment protecting, energy saving and recyclable, and is strongly supported by relative national policies, which makes it an emerging industry with infinite possibility.
-
Aerated concrete is a kind of wall panel material and has good thermal insulation capability, can satisfy the energy saving requirement without adding other materials. Compared with the widely used thermal insulation material, such as EPS thermal insulation mortar and common foam polystyrene panel, aerated concrete has the following advantages, high quality, easy to use, long life span, high cost performance, etc.

Aerated concrete refers to the light porous silicate product manufactured by setting siliceous materials (sand, coal ash and tailings containing silicon) and calcareous materials (lime and cement) as principal raw materials, and adding foaming agent (aluminum powder) after batching, stirring, pouring, pre-curing, incision, steam pressing and maintenance. Containing a large number of uniform and fine pores after foaming, it is called aerated concrete.

-
Lime – coal ash aerated concrete
-
Lime – sand – cement aerated concrete
-
Lime – siliceous tailings–cementaerated concrete
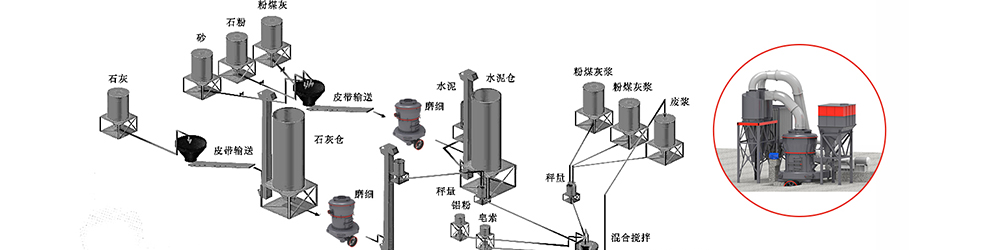
Raw materials of aerated concrete can be divided into four types: basic material, foaming material, adjustment material and structural material.Among them, basic material, foaming material and adjustment material all have different fineness requirements, so grinding is often needed, such as:
-
Lime
180-200 meshes
D90-D85
(coarse particles are prohibited) -
Coal ash
325 meshes
D55-D70
(180meshes, D75-D85) -
Aluminum paste
200 meshes
D97
See standard JC / T621, JC / T409, JC T407 / etc.

Quick lime grinding: Quick lime after burning should be crushed via jaw crusher at first, and then enter the surge bunker through the elevator. After that, Block materials in the surge bunker would be fed into the grinding host of Euro-type grinding mill through the vibrating feeder. After grinding in the grinding host and screening by classifier, the powder will be collected in the powder collector. Lastly, the powder collected will enter the raw material storage tank of aerated concrete via the elevator or pneumatic transmission equipment. (The process of preparing powder like coal ash, gypsum and slag is similar to the process of preparing quick lime powder. And whether to select crushing system is determined according to the raw material granularity.)
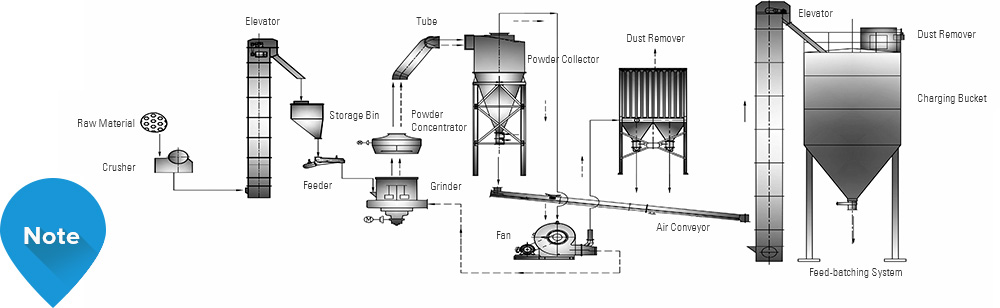
Fine quick lime powder, rather than slaked lime, is often used to produce aerated concrete. As for the reason, when quick lime powder is digested, a large amount of heat will be produced, which will promote the generation of hydrated gel. Meanwhile, the manufacturing technique can be controlled, and the product quality can be guaranteed.
Raw materials of producing aerated concrete, such as cement, gypsum, lime, coal ash or sand, will be stored or crushed, grinded and reserved in different storage warehouses; then they will enter the stirring system for mixing and stirring with additives like aluminum powder and water after measurement. After stirring, it will enter the static system for foaming and maintenance. Later incision will be conducted according to the production requirements. After the above steps are completed, it will be put into the steaming reactor for autoclaved curing and last be packaged.